Total joints replacement - knee joint
Anatomy
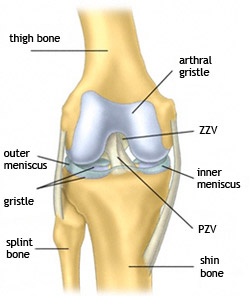
The knee joint connects the two longest bones of the human body, the thigh bone and the shin. In motion it is subject to enormous lever forces. Its stability is provided by a complicated fibrous apparatus. This apparatus is considerably vulnerable. The knee joint often shows marks of degenerative afflictions due to many injuries and distinct functional load.
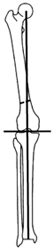
Ideal loading of the knee joint run on the mechanical axis of a limb, thus on the direct line of the thigh bone head, the centre of the knee joint and the centre of the ankle joint.
Arthritis of the knee joint (gonarthroses)
It is degenerative non-inflammatory affliction of the knee joint hyaline gristle showing itself as its flattering, creation of joint osteophytes, bone sclerosis and changes of soft tissues. It is clinically found as pains in movement, changes of the limb axis, rigidity of joints. The starting pain in the beginning of a movement and the morning pain are typical symptoms.
Primary coxarthrosis – it is risen on the basis of gristle metabolic disorder
Secondary coxarthrosis – the original cause is not primarily on metabolic basis
Possible causes:
- various injuries (of a gristle, a fibrous apparatus)
- arthrosis, (conditions after joints inflammation)
- inborn and developed deformations
- axis deformities
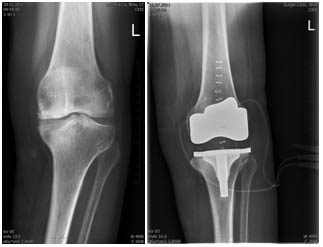
Gonarthrosis on X-ray pictures shows itself as successive narrowing of the articulated joint and growth of fringe osteophytes, as subchondral sclerosis, sometimes even as creation of subchondral cystis with possibility of creation of bone necroses. Arthrosis shows itself at four stages according to X-ray pictures.
Surgical treatment
Debridement of a knee with arthritis
During earlier stages of knee arthrosis it is suitable to use athroscopic revision of the joint, when it is possible to treat degenerative elastorrhexis of meniscus, to smooth peeling gristle, to remove free bodies or eventually revive areas of local gristle defects.
Corrective osteotomy
If the lower limb axis is changed due to abrasion of the gristle, in indicated cases it is suitable to compensate the load distribution on its surface by its correction, called corrective osteotomy.
Alloplastic – artificial joint
Alloplastic of the knee joint is a replacement of a deformed joint with a surgical implant.
Femoral components– mostly metal (CrMoCo steel), fixed with bone cement
Tibial components– usually from titan, fixed with bone cement
Tibial plateau– polyethylene sliding surface between femoral and tibial components
Preoperative preparation
Before the alloplastic of the knee joint it is important to examine a patient thoroughly. We practise standard preoperative examination in our Grand Class ambulance (EKG, laboratory tests, X- ray examination of the heart and lungs), dental, gynaecological and urological examination. In preoperative period it is needed to control medication of the drugs, influencing blood coagulation. A patient gets axillar crutches and medication to prevent thromboembolic disease.
Surgery
A patient spends in the chart room approximately 120 min. The patient is always guided by a physician anaesthetist and a nurse anaesthetist. In most of the cases it is suitable to perform the alloplastic of the knee joint under spinal anaesthesia, so the patient is conscious during the surgery. Only the operated limb is insensible. To evoke pleasant atmosphere patients are given sedatives. The surgery itself takes approximately 90 min. To replace the lost blood it is used recuperation, the blood sucked from the wound is returned back to the blood circulation after special treatment. It is not often necessary to transfer blood of another person or to perform auto transfusion.
At our SurGal Clinic we can accomplish the implantation of the knee joint by means of the Visionaire method. Our workplace is one of the three centres in the Czech Republic.
Postoperative treatment
A patient goes from the chart room to the postoperative department (Intensive Care Unit), where his/her state is monitored for approximately 24 hours. Further treatment then usually takes place on standard and extra beds of our institution. During after-treatment stay the patient is visited by experienced physiotherapist who leads the rehabilitation. Patients are within one week mostly so mobile and independent that they can be transferred to another place. Stitches removing is recommended on the 12. – 14. day of the after-treatment. Patients visit our ambulance for regular check-ups in the 1, 3, 6, 12 month after the surgery. In the period of one year they can choose sequential therapy in a health-resort. Subsequently they are regularly observed every year.
Complications and risks
Complications can arise after every surgery, still they are successfully reduced to minimum through modern techniques and materials and high specialization of the physicians.
The most common complication of alloplastic of the knee joint is secondary healing and longer time taking serosal wound ooze. In most of the cases it is enough to rebind the wound regularly, eventually to dose antibiotics. If the inflammatory parameters rise in the cultivated infectious agent, it is sometimes necessary to undertake a corrective surgery of the joint.